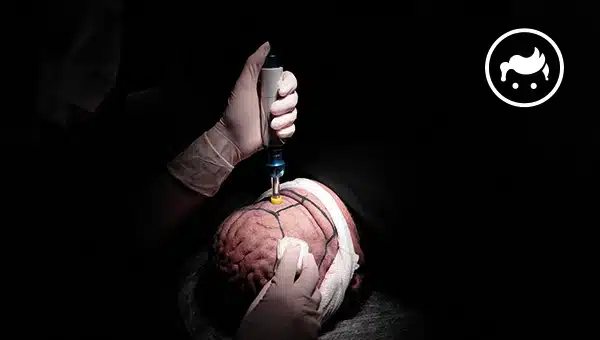
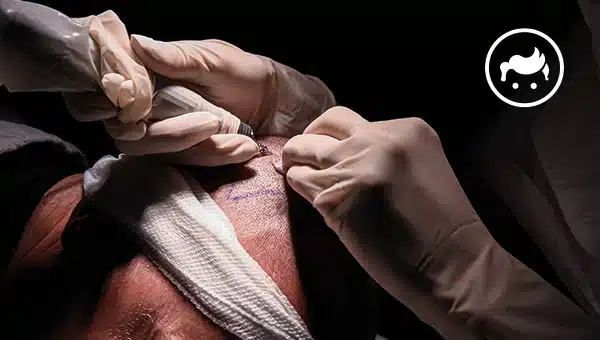
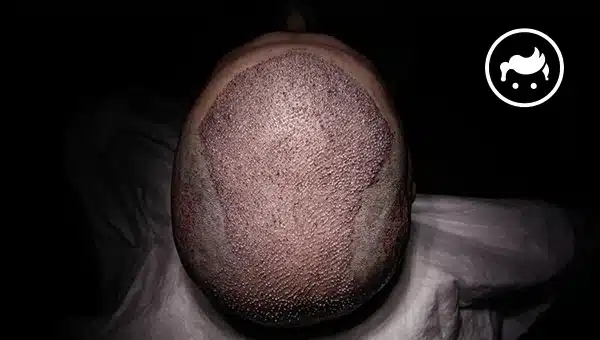
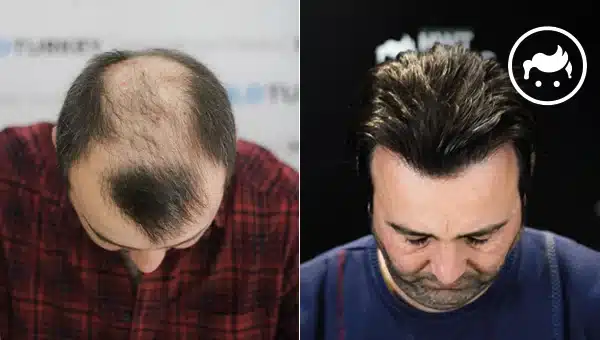
There are advantages and disadvantages of hair transplants. The advantages of the hair transplant are permanent, natural-looking effects, restoring self-confidence, cost-effectiveness, and combination with other procedures. Meanwhile, the hair transplant's disadvantages are its healing time, needs maintenance, the risk of complications, its cost, possible unsatisfactory effect, and the surgical approach itself. Moreover, a hair transplant is for those who encounter hair loss because of some circumstances, such as male and female pattern baldness and scarring alopecia. There are things to know about hair transplant procedures, including the techniques, determining the goals, the method, and its dangers. Furthermore, hair transplants started in the 1800s when Charles Miller conducted the first recognized hair transplant procedure. On the other hand, other cosmetic methods similar to hair transplants are scalp reduction surgery, hair integration, micro scalp pigmentation, and laser hair restoration. A few alternatives to hair transplant surgery include laser therapy, platelet-rich plasma, scalp micro-pigmentation, medication, and wigs and hair pieces. Meanwhile, hair transplant has various side effects, and the three main adverse effects are infections, bleeding, and swelling.
What is a Hair Transplant?
A hair transplant is an approach where the hair follicles out of a part of the body are transferred to a bald-headed or hairless part. The body where the hair follicles come from is referred to as the “donor site,” while the bald or becoming bald part is referred to as the “recipient site.” The back of the head is generally the donor site because it is the part where the hair is more immune to balding. It is an approach to address hairlessness. Hair transplant surgery aims to address bald heads in males and females and revive sites in other body parts, including brows, lashes, and beards. Baldness is a common reason for hair loss. Hair transplant surgery revives hair to parts of the scalp damaged because of injury, operation, or other medical circumstances.What are Hair Transplant Holes?
Hair transplant holes are holes in the head section where the hairs are placed. The physician forms a little slit, like an opening in the recipient site, where the acquired grafts are embedded. They use scalpels or other operative instruments to create minor cuts in the recipient area. The holes have a similar tilt, slant, and direction as the client's hair to position the hair follicle tissue inside. The hair transplant holes are noticeable subsequently to the surgery; nevertheless, they must rapidly heal.
What is Hair Transplant Procedure?
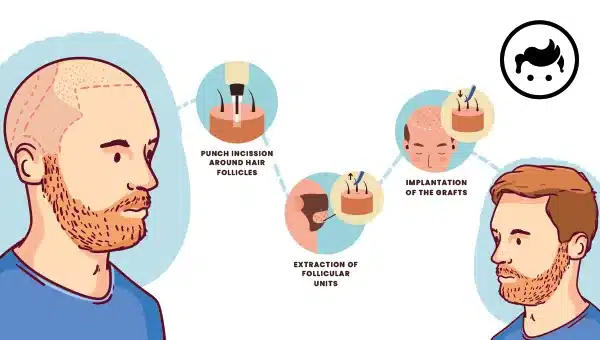
Turkey hair transplant procedure includes carrying hair from the donor site to mend where the hair is thinning or fully bald. It is executed by gathering single hair follicles one at a time with a small, powered punch or removing a strip of scalp grafts with hair and closing the site with stitches or sutures. Nevertheless, hair transplant is only for some. It needs sufficient donor hair to give the thinning or hairless areas. The donor hair muse has healthy hair follicles.What are the Steps for Hair Transplant Treatment?
• Interview: The surgeon needs to interview the client and assess their hair growth and loss. They are going to ask about the family history of hair loss and know if there are any past hair transplant surgeries, as well as the client's lifestyle and diet. It is when the surgeon and the clients talk about the desired outcome and goals for the surgery. The assessment enables the surgeon to judge the volume of hair grafts required to attain a natural look.
• Preparation: The things to do to prepare for the Turkey hair transplant treatment are head massages, keeping out of the sun, no drinking, no supplements, no smoking, no Tylenol, stop taking hair loss remedies, and do all surgeon's orders.
• Injecting anesthesia: Hair transplant treatment needs dependable anesthesia for an extended period. The procedure is usually conducted under anesthesia to make the area insensible and lessen the pain. A 1ml to 3ml local anesthesia is injected. Keep the pressure on the injected site to drench nerves and attain hemostasis once the needle has been withdrawn. It is effective if the numbness is up to the top of the head.
• Collecting hair and follicles: Collecting or harvesting starts with planning and finishes with delivering hair and follicles prepared for grafting. There are two methods of harvesting, such as the follicular unit transplantation (FUT) method and the follicular unit extraction (FUE) method.
• Preparation of grafts: The hair grows in 2 or more clusters. The technicians attentively break down the donor strip using the stethoscope into slivers one follicular wide. It requires a highly-trained staff to prepare to prevent the hair from damaging. They are going to define what follicular configuration is needed, whether larger grafts of multiple follicles, micro grafts of two or three follicles, single-follicle grafts, or follicular units comprising naturally occurring clusters of three or sometimes more follicles. They are going to trim the hair follicles and place them in a solution to keep them alive. The harvested hair follicles are ready for grafting.
• Insertion: The surgeon is going to make minor cuts in the receiving area and insert the grafts into the incisions. They are carefully placed in a particular direction and angle to look natural. The depth of the cuts must be perfect for receiving the graft and ensuring the provision of blood for the follicle. The hair follicle is going to produce new hair with enough blood supply. They must be perfect in size to ensure that they are not small or large for the implanted graft.
• Recover: It is normal for the area to be swollen after surgery. The surgeon is going to inject triamcinolone to lessen the swelling. The physician is going to prescribe medication to help alleviate the pain and swelling. It is necessary to follow the doctor's order for post-operative care, including avoiding strenuous activities. Attend the follow-up check-up for the wound. It takes approximately several months before the result of the hair transplant is entirely noticeable.
Get Your Hair Back with Best Hair Transplant Surgery

What are the Possible Hair Transplant Side Effects?
• Bleeding: It is normal to experience bleeding during the day of the procedure since it is a surgical operation. The surgeon usually makes sure that the bleeding is at a minimum during the process, but there are times that there is bleeding in the donor site that must stop once the pressure is applied. The bleeding area is going to heal after the next few days or weeks. It is essential to visit the physician once the bleeding is continuous the day after the procedure.
• Infection: There is a risk of infection in any surgery. It is essential to perform the procedure in a sanitized surgical room to lessen the risk. The infection usually begins the day after the process. The causes of infection to the scalp are feeling hot, itching, and painful yellow bumps. The treatment for infection is antibiotic and must cure the infection within seven days.
• Crusting: Crusting is normal and occurs on the donor and recipient sites. The crusts are the dried blood and fluid from the surgery established around every implanted hair. However, it is avoidable if the surgeon meticulously washes and sprays the area during the surgery.
• Itching: It is a natural reaction to the healing area and an average side effect of significant operation procedures. Nevertheless, it is able to damage or dislodge the newly implanted delicate follicles. It is usually the last side effect and frequently impacts the back and sides of the head where the donor site and the recipient site are. Itching takes place four to five days after the procedure and takes up to a month.
• Pain: The pain worsens at night or the day after the procedure. It is usually on the donor site as well as on the recipient site. The patient is going to feel minor cuts on the head once the effect of the local anesthesia has worn off. Mild pain is one of the common side effects of PRP injection for hair. It takes one to two weeks to recover from the pain.
• Hair loss: It is known as “shock loss.” It is the normal side effect of FUE hair transplant surgery. It happens one week after the procedure. The new hair starts to grow in about eight to twelve months once the extravagant dropping of hair stops.
• Scars: Scarring appears after the hair transplant surgery. However, it is typically minimal and concealed by the hair. Every extraction leaves a small round scar. It looks like small white dots following the healing.
• Swelling: Swelling is one of the side effects of a hair transplant. It is called 'oedama'.The typical swelling area is the forehead, and it usually takes two to six days before swelling down. Inflammation is an element after the surgery. The skin tissue in the scalp swells and feels stiff because of inflammation. The eyes are sometimes affected.
• Folliculitis: Folliculitis is one of the 10 Hair Transplant Side-effects of hair transplant surgery. A string of pimple-like bubbles occurs on the recipient site, which results in itching. It disappears in some days with the application of the solution to maintain the recipient site well-moisturized.
• Unsatisfactory outcome: There is a small risk that the outcome is unsatisfactory. Some elements impact the surgery's result, including the volume and quality of the donor's hair, the ability of the physician, and the client's reaction to the surgery.
A Turkey hair transplant's three main side effects are infections, bleeding, and swelling. Infections are one of the risks of any surgery. It is essential to follow the post-surgery care instructions given by the surgeon to lessen the dangers of a hair transplant. Additionally, bleeding is common during and after a hair transplant treatment; however, excessive bleeding is able to lead to complications. Furthermore, scalp, neck, and face swelling is a usual side effect of the Turkey hair transplant procedure. It commonly diminishes after a few days or a week following the surgery. On the other hand, the rarest side effects of hair transplant surgery are allergic reactions to the medications or products applied during the surgery, the formation of cysts, blisters at the transplant area, hair loss at the implanted site, scarring, and constant pain.
What are the Success Factors for Hair Transplant Treatment?
What are the Types of Hair Transplant?
• Follicular Unit Transplant (FUT): It strips the skin with hair follicles from behind the head and implants it to the recipient area. An operative knife or dermatome is necessary for a Follicular Unit Transplant (FUT).
• Follicular Unit Extraction (FUE): The hair follicles are withdrawn from the back of the head one at a time using a unique tool. It does not remove a strip of skin; instead, they use a small punch.
• Platelet-Rich Plasma (PRP): It is from the removed blood of the person and vaccinated into the body part that wants to be treated. They use an extractor to divide the platelets and plasma out of the other blood cells.
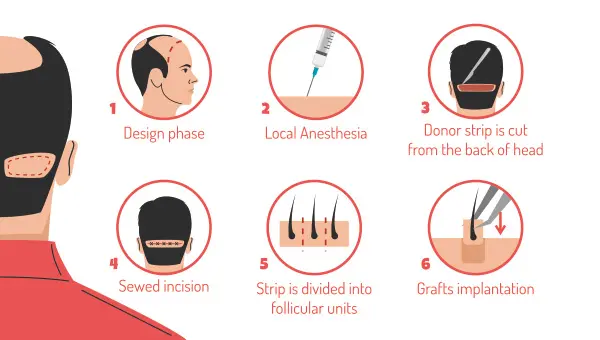
1. Follicular Unit Transplant (FUT)
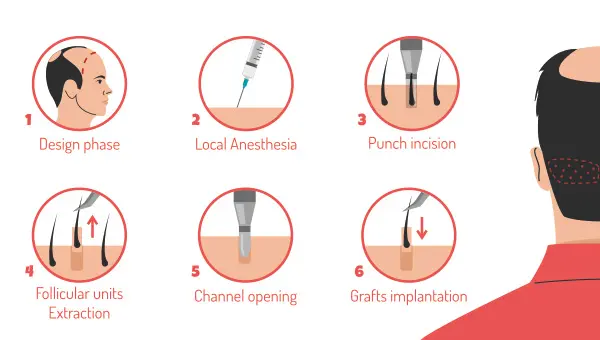
2. Follicular Unit Extraction (FUE)
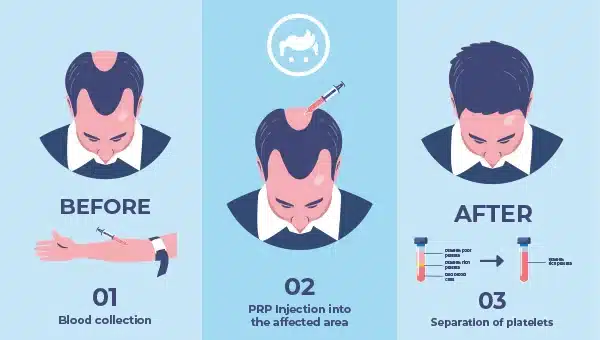
3. Platelet-Rich Plasma (PRP)
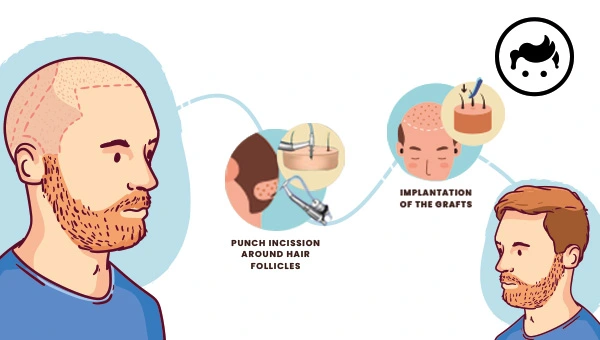
What is NeoGraft?
What is Hair Graft and Grafting?
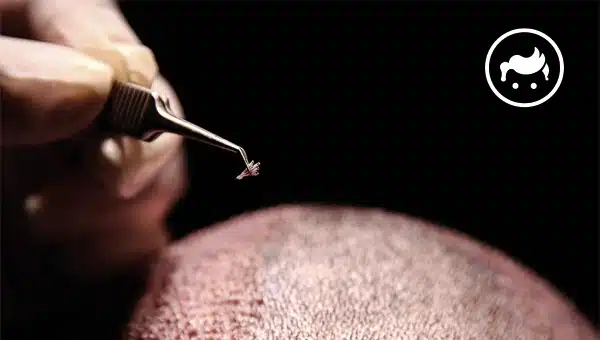
How are Hair Grafts Acquired for Hair Transplantation?
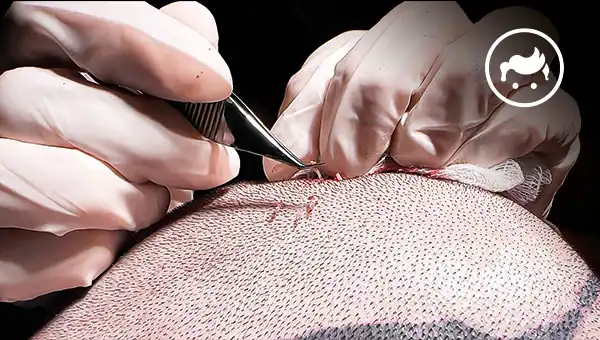
What is the Most Popular Hair Restoration Technique?
Does Hair Transplant Surgery Change According to Hair Type?
How to Prepare Yourself for Hair Transplant Treatment?
- Study the options: There are different techniques for Turkey hair transplant surgery. It is essential to study and understand each option available, including its risks and benefits. It is time to research clinics once the patient is decided on what treatment they think they want. The clinic must be near the house.
- Look for a reliable surgeon: It is essential to look for a qualified and skilled hair transplant surgeon with a good track record. There are things to consider in looking for a surgeon, such as their specialization, years of experience, number of procedures they have conducted, and credentials.
- Discuss the desired outcome with the surgeon: It is essential to tell the surgeon about the desired effect and expectations. Let them know all the information, including the history of hair loss.
- Obey the pre-surgery instructions: The surgeon is going to give instructions on Preparing for Hair Transplant Surgery, including no drinking, no supplements, no smoking, no Tylenol, stop taking hair loss remedies, head massages, keeping out of the sun, and following all surgeon’s orders.
- Organize transportation and support: The person having surgery needs a companion after the procedure because they are not able to drive. It is a must to arrange for someone to stay with the patient for at least the first day after the surgery to give support and help as needed.
- Maintain good health: It is vital to maintain good health by eating a healthy diet, getting enough sleep, and avoiding unhealthy habits, including alcohol or smoking. They help enhance the recovery process after the procedure.
How to change Diet for Hair Transplant Treatment?
- Eat nutrient-rich foods: Nutrient-rich foods are beneficial for the healthy growth of hair, including protein, iron, and vitamin C and A. Ensure to eat some vegetables, fruits, healthy fats, whole grains, and lean proteins.
- Drink lots of water: Drinking lots of water helps the hair and scalp to stay hydrated. Make sure to drink at least 8 ounces of water every day, aside from
- Get adequate protein: Protein is helpful to make the hair healthy because it helps to establish and fic tissue. Protein-rich foods are nuts, beans, lean meats, fish, eggs, and poultry.
- Avoid processed and sweet foods: Processed and sweet foods are high in empty calories and do not have essential nutrients for healthy hair growth. Restricting the intake of unhealthy foods helps improve the hair's whole health. It is important to know what to eat to help the outcome of the procedure be successful.
- Eat iron-rich foods: Foods rich in iron are beneficial for healthy hair growth. The foods that are good sources of iron include leafy green vegetables, red meat, poultry, beans, and fish. Iron is one of the answers if asked, “What Should You Eat After Hair Restoration Surgery?”
Does Hair Transplant Treatment Affect Hormonal Balance?
Can I Use Drugs After Hair Transplant Treatment?
What are the Advantages of Hair Transplant?
• Permanent: Hair transplants are a lasting answer for hair loss. The embedded hair is immune to the elements that trigger hair loss, including male pattern baldness and genetic inclination. However, it needs broad maintenance.
• Natural-looking outcome: Added advantage of Turkey hair transplant is that it produces natural-looking effects as the hair is from its head; thus, it matches the natural hair’s color and texture. It allows the hairline looks completely natural.
• Restore self-esteem: Hair loss is an upsetting encounter, and a hair transplant helps revive self-confidence by restoring a fuller head of hair.
• Cost-effective: Regular hair repair products are expensive, and it takes a lot of money to achieve the desired result. One is able to save money over time when one stops the demand and usage of other products, even though a hair transplant comes at a higher price.
• Able to combine with other treatments: The Turkey hair transplant procedure is able to integrate with other therapies, including medication or scalp micro pigmentation, to enhance the outcome further.
What are the Disadvantages of Hair Transplant?
• Recovery time: The recovery time for the Turkey hair transplant varies; it includes some side effects, such as pain, swelling, and bruising; thus, it needs time to rest and take some time off work or other activities. The infection often increases when the patient doesn't take the recovery time seriously. Additionally, some are able to go back to their normal activities within one or two weeks.
• Maintenance: Regular maintenance is needed for the transplanted hair, such as shampooing and styling, to keep it looking its best.
• Risk of complications: There are complications in hair transplant treatment, including infections and scarring. However, infections are relatively rare. Most conditions aren't severe; however, it is essential to visit the doctor once an infection occurs.
• Cost: Hair transplant is expensive if the patient must undergo many procedures or has a large area to be treated.
• Unsatisfactory results: There is a small risk that the outcome is unsatisfactory. Some elements impact the development of the surgery, including the volume and quality of the donor's hair, the ability of the physician, and the client's reaction to the surgery.
• Surgical procedure: The procedure itself is one of the disadvantages of hair transplant, which makes some patients terrified and scared. However, physicians do their best to help the patient to calm down and relax before, during, and after the procedure.
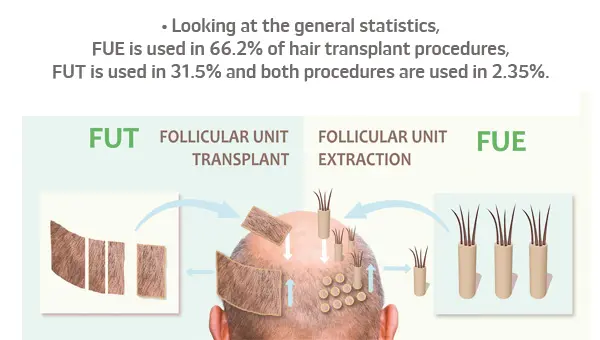
What are the Hair Transplant Statistics?
• Percentage of FUE and FUT: Follicular Unit Extraction (FUE) is applied in 66.2% of hair transplant techniques. Meanwhile, Follicular Unit Transplantation (FUT) is applied in 31.5%. Both methods are applied in 2.35%. The most typical method for a hair transplant procedure is (FUE), in which particular hair follicles are gathered and implanted in the wanted area.
• Percentage of male patients: The percentage of male patients who have undergone hair transplants is 87.3%, based on the International Society of Hair Restoration Surgery in 2024. Hair transplant is most typically executed on men, but a rising number of women also aim for hair transplant procedures.
• Percentage of people’s reasons who have undergone hair transplants: The reason for hair loss of 37% of people who have experienced hair transplants is because of social life and relationships, 34% for the profession and 14% do not have any reason.
• Popularity: Hair transplant surgery is a widespread cure for hair loss, with around 500,000 techniques conducted around the world annually.
• Success rate: The success rate for hair transplant techniques is commonly high, with most clients encountering notable progress in the formation of their hair. About 10% to 80% of implanted hair is going to grow back in approximately 3 to 4 months fully.
• The average rate of hair transplants in Turkey: The average rate of hair transplants in turkey ranges from 1,250€ to 4,300€. Turkey hair transplant cost procedure varies widely depending on the method used, the scope of the procedure, and the place where it is executed. Costs range from a few thousand dollars to tens of thousands of dollars.
• Age: 87% of the clients who have undergone hair transplants were between 26 and 45 years old.
• Hair transplant on different body parts: Professionals transplant the hair on other parts of the body. 89% of hair transplant in male is on the scalp, 4% on the beard, and 3% on the eyebrows. Hair Transplant Statistics in females vary. 79% of hair transplant in female is on the scalp, and 15% are on the eyebrows, according to the data from the International Society of Hair Restoration Surgery.
What are the Best Hair Transplant Researches?
• 'Hair transplantation' by Norman Orentreich: It was released in 1959. It is continually deemed the primary progressive hair transplantation research. It presented the idea of 'donor dominance,' which pertains to the notion that implanted hair maintains its authentic attributes and keeps increasing even when transferred to a distinct area on the scalp.
• 'Predictors of success in hair transplantation' by Walter P. Unger: It was released in 1995. The research pinpointed several elements that impact the positive effect of hair implantation, such as the thickness of the donor area, the adaptability of the scalp, and the general health of the hair and scalp.
• 'Follicular unit extraction: Minimally invasive surgery for hair transplantation' by Carlos Uebel and Rolf Hamm: It was released in 2002. The research presented the thought of follicular unit extraction (FUE). FUE is an approach for gathering particular hair follicles from the donor site utilizing an undersized punch instrument. It evolved as a widespread alternative to the usual strip approach of hair transplantation.
• 'Hair transplantation for androgenetic alopecia: Patient satisfaction and self-perceived changes in quality of life' by Jennifer Lee et al.: It was released in 2013. The study interviewed clients who had experienced hair transplantation for androgenetic alopecia (male or female pattern baldness) and discovered that most of them said their self-esteem and quality of life after the procedure bettered.
What are the Hair Transplant-related Concepts and Definitions?
• Androgenetic Alopecia (Male Pattern Baldness): Androgenetic Alopecia (Male Pattern Baldness) is a usual form of hair loss in males and females. The interaction of hormones, age, and genetics causes it. It decreases the hairline and thinning of the hair on the crown and top of the head. Most men over 30 years old experience Androgenetic Alopecia, which is deemed hereditary. It is not necessary to cure it because it is not a severe condition. Learning about Androgenetic Alopecia is essential for anyone planning hair transplant surgery, as it helps to define the ideal treatment choice.
• Autograft: An autograft is a form of tissue transplantation in which it is moved from one part of the body to another. It is usually used in many medical procedures, such as burn treatment, plastic surgery, and hair transplant. Autograft provides a natural-looking outcome and is able to be more simply merged into the patient's existing hair. It is the preferable type of tissue transplantation. Autograft is not suitable for everyone. However, its necessity depends on the particular medical procedure and the patient's needs and circumstances. Knowing about Autografts is beneficial for anyone who wants to undergo medical treatment, including tissue transplantation.
• Allograft: An Allograft is a form of tissue or organs attained from a donor and implanted of the same species but who is not naturally connected to the donor. It is used to change destroyed or unwell tissues or organs in the recipient. There are three types: whole organ allografts, tissue allografts, and stem cell allografts. Allografts' necessity relies on the recipient's specific medical needs and the accessibility of suitable donors. Individuals with severe health issues and need of tissue or organ substitution. Additionally, it is essential to know allografts' principles and possible risks and advantages.
• Bulge Area: The bulge is a body part with protrusion or swelling. It is able to appear in many parts of the body, including the abdomen, arms, and legs. The cause of bulges is muscle development, pregnancy, weight gain, or accumulation of fat or fluid. Additionally, the necessity of the bulge area relies on the particular circumstances in which it appears. It is essential to know bulge areas in the body as they are likely signs of underlying health problems.
• Camouflage: The camouflage technique pertains to the ways used to cover the appearance of scarring or thinning hair. It is used to enhance the overall look of the scalp. It is helpful for people who underwent hair transplant surgery or thinning hair because of medical circumstances, including Alopecia. Additionally, the necessity of camouflage technique in hair transplantation relies on the particular demands and objectives of the person. Some individuals prefer to use camouflage techniques to enhance the appearance of their scalp after the hair transplant procedure, while others use the method to cover thinning or balding hair. It is essential to know as they are able to improve the look of the scalp and boost self-esteem.
• Club Hair (Telogen hair): Club Hair (Telogen hair) is a hair type in the resting phase of the hair growth cycle. The hair growth cycle has three phases: anagen, catagen, and telogen. A club hair is usually on the scalp and loos as thin, short, and lifeless hair. The hair stops growing during the telogen phase, then sheds after a few months, and is changed by new hair in the anagen phase. Club Hair (Telogen hair) is a natural and necessary part of the growth cycle. A club hair is needed to function the hair follicles and scalp properly. It is essential to understand Club Hair (Telogen hair) as it helps to keep the health and look of the hair and scalp and determine any potential underlying medical problems that need to be solved.
• Companion Layer: The cells surrounding the hair shaft are called the companion layer, which gives structural support to the hair follicle. It is made up of cells referred to as trichocytes. Trichocytes create the keratin protein that makes up the hair shaft. The companion Layer is situated within the internal and external root sheath and is accountable for keeping the shape and integrity of the hair shaft. Additionally, it is a vital part of the hair follicle that plays an essential role in hair growth and function. The necessity of the Companion Layer relies on the whole health and function of the hair. A healthy and working companion layer is essential for the appropriate development and hair's look. It helps to determine any potential problems with the hair.
• Dermal Papilla: Dermal Papilla is a small and finger-like projection of cells that extend from the dermis, the middle layer of the skin. It is in the hair follicles and essential for the growth and development of hair. It contains stem cells that assist in rejuvenating hair cells and consist of blood vessels that give hair nutrients. Dermal Papilla plays its part in establishing the hair shaft, the visible part of the hair that stretches above the skin. Additionally, Dermal Papilla requires various factors to function appropriately, such as nutrients, blood flow, hormones, growth factors, and stem cells. It is essential to know and understand Dermal Papilla because it is helpful in dermatology and advancing treatments for hair loss or other hair-related circumstances.
• Dissection: Dissection is a process where the surgeon uses a specialized dissecting microscope to separate the hair follicles from the meticulously surrounding tissue. It is usually used in the FUE technique. The hair follicles that are dissected are inserted into tiny cuts in the recipient site. Dissection decides the quality and viability of the hair follicles that are going to be implanted, making it a crucial step. The necessities to successfully perform the dissection process are the surgeon's expertise, a sterile environment, surgical tools, patient preparation, and enough lighting. Additionally, it is essential to know about dissection because it is a crucial step in hair transplantation and to be able to have a successful procedure.
• Donor Area: The donor area is part of the scalp where the gathered hair follicles come from for implantation to a bald or thinning area called the recipient area. The donor area is usually situated at the back or sides of the scalp. It is necessary that the donor area is healthy and have enough supply of hair follicles to have a successful hair transplant. Other necessities of the donor area are good quality hair, stable hair growth, thick scalp tissue, a good blood supply, and no scarring or scarring that is able to be covered. It is essential in hair transplant procedures because it defines the availability and quality of hair follicles for surgery. Another importance is it determines the method to use and the volume of grafts needed.
• Donor Density: The donor density refers to the volume of hair follicles every square centimeter in the donor site. It is one of the essential factors in determining the availability of hair follicles used for the transplant. A considerable volume of hair follicles every square centimeter in the donor site is called high donor density, making removing sufficient hair follicles simpler. Meanwhile, fewer volume of hair follicles every square centimeter is called low donor density. The necessities of the donor density rely on the patient's particular needs and goals and the donor site's quality.
• Donor Dominance: Donor Dominance is a hair transplant procedure concept that pertains to the ability of the implanted hair to keep its genetic qualities after the surgery. It is an inequality of power wherein the donor shows dominating behavior that consists of an organization's task and its skill to serve its beneficiaries. The back and sides of the scalp are more dominant and more immune to thinning and balding than hair transplanted from the other areas of the scalp. Knowing the donor dominance is able to help the surgeon define the workability and anticipated outcome of the hair transplant surgery and choose the best hair transplant technique for the client.
• Finasteride/Dutasteride: Finasteride/Dutasteride are drugs used to treat male pattern baldness and benign prostatic hyperplasia (BPH). They function by obstructing the enzyme 5-alpha reductase, which is accountable for turning testosterone into dihydrotestosterone (DHT). DHT is a hormone linked with male pattern baldness and prostate gland growth. The brand name of Finasteride is Propecia, while Dutasteride is Avodart. The necessities for using Finasteride/Dutasteride rely on the particular condition being treated and the individual patient. However, the primary need for using the medications is the appearance of male pattern baldness. It is only for men. It is important to know the information about the risks and benefits of Finasteride/Dutasteride before taking them.
• Follicle: A follicle is a small, sac-like structure that contains the cells that create hair. Every hair on the scalp develops from a small-tube-like form referred to as the hair follicle. The hair follicle is rooted in the scalp and stretches down into the dermis, the skin's deeper layer. Various forms make the hair follicles, including the hair shaft, bulb, and matrix. The hair follicles are surrounded by a network of blood vessels and nerve fibers that support the health and growth of the hair. Maintaining healthy hair follicles requires enough nutrients and hydration, proper scalp care, and minimizing damage. Knowing the follicle is beneficial in identifying the best treatment choices for hair loss and thinning.
• Follicular Unit: Follicular Unit is a naturally occurring group of hair follicles in the scalp. Every follicular unit has one to four hair follicles, sebaceous glands, and arrector pili muscles. It is surrounded by a network of blood vessels and nerve fibers that encourages the health and growth of the hair. They are essential for hair transplant surgery as they are the fundamental unit of hair growth. It enables the surgeon to make a natural-looking outcome by copying the natural arrangement of the hair on the scalp and electively implanting only the hair follicles needed.
• Follicular Unit Dissection: Follicular Unit Dissection is a method in which commonly occurring, single follicular units are dissected from the donor tissue and extracted as individual strips to keep the whole of the follicular units. It is a surgical procedure to rejuvenate hair to the sites of the scalp where it is thinning or balding. The necessity of the Follicular Unit Dissection relies on a person's particular condition and their objective for treatment. Follicular Unit Dissection is essential as it is a potential treatment option for hair loss; it produces natural-looking results; it needs meticulous planning and implementation and has some risks.
• Follicular Unit Graft: The Follicular Unit Graft comprises an individual follicular unit, keeping the direction of hair grown on the scalp. It involves the extraction of a strip of skin from the scalp and separating it into single hair follicles or follicular units. The procedure depends on the condition. Some people who experience hair loss have the option to undergo follicular unit grafting to restore the hair and enhance the look.
• Follicular Unit Extraction (FUE): Follicular Unit Extraction (FUE) is a hair transplant type and sutureless procedure in which the patient's hair follicles are removed from the back of the head one at a time using a particular instrument. The harvested follicles are transplanted in the desired recipient site, typically on the front or top of the head. Additionally, the necessities of FUE are good overall health, enough donor hair, realistic expectations, dedication to post-procedure care, and the capability to pay. Follicular Unit Extraction (FUE) is essential as it is a potential treatment option for hair loss; it produces natural-looking results; it needs meticulous planning and implementation and has some risks.
• Follicular Unit Transplantation (FUT): Follicular Unit Transplant (FUT) is a hair transplant type in which a strip of the skin consisting of hair follicles is removed from the back of the head; then, the individual hair follicles are separated and transplanted the recipient area. The instrument needed to do the procedure for Follicular Unit Transplant (FUT) is a scalpel or dermatome. Additionally, the necessities of FUT are good overall health, enough donor hair, realistic expectations, dedication to post-procedure care, and the capability to pay. Follicular Unit Transplantation (FUT) is important as it is a potential treatment option for hair loss; it produces natural-looking results; it needs meticulous planning and implementation and has some risks.
• Follicular Unit Hair Transplantation (FUHT): Follicular Unit Hair Transplantation (FUHT) is a method of hair restoration that includes the extraction of single hair follicles from the scalp and transplanting them to sites of the scalp where thinning and balding occurs. The different procedures that are able to use to perform FUHT are Follicular Unit Transplant (FUT) and Follicular Unit Extraction (FUE). The necessities of FUHT are a skilled and expert surgeon, the right donor area, a healthy scalp, realistic expectations, and time and dedication. Some of the reasons why FUT must be known include natural-looking outcomes, high success rate, long-lasting outcomes, non-invasive, and safe.
• Follicular Pairing: Follicular Pairing is a surgical technique used in hair transplant surgeries, such as FUHT. It aims to optimize the volume of implanted hair follicles that are able to be gathered from the donor site and embedded at the recipient site. The physician meticulously pairs two or more follicular units that are naturally growing together in the donor site. Follicular Pairing is used when the donor area has insufficient hair density to meet the demands of the recipient area. The necessities of Follicular Pairing include a high level of skill and accuracy and must be conducted by a skilled and expert surgeon. Some of the reasons why Follicular Pairing must be known include enhanced outcomes, greater efficiency, modern technique, and alternative option.
• Front of Scalp: The Front of the Scalp is the part of the head located at the front of the forehead and above the eyebrows. It is referred to as a hairline. Some of the fronts of the scalp are prone to hair loss or thinning because of a few elements, including genetics, age, and other medical conditions.
• Graft Excision: Graft Excision is a surgical procedure removing the graft or piece of tissue implanted from one part of the body to another. It is essential if the graft has become infected, has not been taken appropriately, or is causing other issues. Graft Excision is conducted using a scalpel and done under anesthesia. Graft Excision is necessary for possible infection of grafts, rejection of grafts, poor healing, and complications. Graft Excision is needed for specific conditions and to look at as a means of addressing particular medical problems.
• Grafts Cut to Size: Grafts Cut to Size pertain to preparing a piece of tissue or graft for transplantation by cutting it to the correct size and shape for the intended recipient's site of need. It allows for an accurate, appropriate result explicitly created to enhance the success rate of the surgery. Expert physicians depend on the procedure to give their clients unique, tailored solution that meets their personal needs. Grafts Cut to Size is necessary because it lessens the scarring and pain and is a secure and firm fit for individual needs.
• Hair Shaft: Hair shaft pertains to the keratinized tissue forming the external concealing of the hair strand. It consists of three layers: the cuticle, cortex, and medulla. The hair shaft is essential because it protects the hair strand's follicles, scalp, and inner forms from environmental damage. Hair shafts must be known as they are an essential form of hair and five strength, durability, and resilience to daily wear and tear.
• Lateral Slits (Coronal Slits, Horizontal Slits): Lateral Slits (Coronal Slits, Horizontal Slits) are tiny openings constructed in the scalp which enable a higher exposure of the underlying skull structures. It allows for the benefit of orienting the hair in the follicular unit to correspond to how it becomes in nature. The grafts inserted with the lateral slit method appear more natural and have the disposition to give an illusion of a higher density of hair than vertically inserted grafts.
• Mid-scalp (Top): Mid-scalp (Top) is a hairstyle technique that includes cutting the hair along the centerline of the scalp, making an even and complementary look. It provides more types than traditional haircuts by permitting creative styling choices, including layers, fringes, or textured bangs.
• Miniaturization: It is a process of hair follicles becoming smaller and producing thinner and finer hair over time. It happens due to several factors, including genetics, aging, and particularly medical situations. The miniaturization of the hair follicles is able to lead to hair loss, and it is often a principal factor in androgenetic Alopecia, which is known as male pattern baldness.
• Micro-graft: Micro-graft is a small graft consisting of one to four hair follicles. They are often used in hair transplantation surgery to make a natural-looking appearance by copying the way hair grows naturally. Micro-graft is usually caused by gathering healthy follicles from the back or sides of the scalp, which are then meticulously implanted in sites of the scalp that are thinning or balding. Some of the necessities of Micro-graft are to restore a natural-looking head of hair, to restore a natural hairline, to restore density and fullness, and to correct previous hair transplantation surgery.
• Mini-graft: Mini-graft are typically prepared after one or more strips of skin are removed from the donor site. They are inserted into cuts on the recipient and are made with a scalpel, needle, or the same device. They are cut to suit the recipient areas. Mini-graft consists of 3 to 8 hairs. Some of the necessities of a Mini-graft are to restore a natural-looking head of hair, to restore a natural hairline, to restore density and fullness, and to correct previous hair transplantation surgery.
• Norwood Classification: Norwood Classification is a system used to explain the stages of male pattern baldness, known as androgenetic Alopecia. It was advanced by Dr. James Hamilton in the 1950s and broadly used to examine the range of hair loss and guide treatment decisions. There are seven stages in Norwood Classification. It ranges from stage 1, which is minimal hair loss, to stage 7, which is severe hair loss. Some of Norwood Classification's necessities are assessing the scope of hair loss, guiding treatment decisions, monitoring the progression of hair loss, and communicating with patients. It must be known as it is an essential concept in dermatology and hair restoration. It is beneficial to know it for various reasons, including understanding male pattern baldness, exploring treatment choices, selecting a healthcare provider, and communicating with expert physicians.
• Post-Hair Transplant Effluvium: Post-Hair Transplant Effluvium is a state that happens after a hair transplantation surgery. It is distinguished by temporary hair shedding that occurs as an outcome of the trauma to the hair follicles during the transplantation procedure. Post-Hair Transplant Effluvium usually happens within the first few weeks or months after the process, and it is able to impact both the donor and the recipient area. However, it is normal and not a sign of failed procedure. The patient must follow the post-operative care instructions to ensure the best possible outcomes from their hair transplant surgery. It is essential to know Post-Hair Transplant Effluvium for patients to understand the hair transplantation process, manage their expectations, follow post-operative care instructions, and look for the proper medical care.
• Recipient Area: The recipient area is the scalp area where hair follicles are implanted. It is usually the part of the scalp that is thinning or balding. The recipient area is generally prepared for hair transplantation surgery by shaving the hair to be treated. It enables the surgeon to see the area clearly and meticulously plan the positioning of the implanted hair follicles. Some of the necessities of the recipient site are to be ready for the hair transplant surgery, to have enough donor hair available, to be in good overall health, and to follow post-operative care directions.
• Senile Alopecia: Senile Alopecia is age-related hair loss. It is a classification of hair loss that is able to appear as an outcome of the aging process. It is distinguished by a progressive thinning of the hair on the scalp. It is able to impact both males and females. Senile Alopecia usually starts to happen in persons in their 40s or 50s. It is able to be managed with treatment choices, such as changing lifestyle and hair restoration process. It doesn't have any particular necessities, as aging is a natural part. However, some things are able considered to manage hair loss, including seeking medical treatment, making changes in lifestyle, using hair care products, and considering hair restoration procedures. It is essential to know about Senile Alopecia as it helps to understand hair loss, explore treatment options, communicate with professionals, and promote overall health and well-being.
• Sagittal Slits (Vertical slits): Sagittal Slits (Vertical slits) are techniques used in hair transplant procedures to make recipient areas for the implanted hair follicles. It includes making a series of vertical slits in the recipient site, usually using a scalpel or a punch instrument, in which the implanted hair follicles are going to be positioned. It is used in the follicular unit transplantation technique, enabling more natural-looking and density-managed allocation of the implanted hair follicles in the recipient site. It is a broadly used technique in hair transplantation surgery and is usually well-permitted by patients.
• Sebum: Sebum is an oily substance produced by the sebaceous glands that are discharged onto the skin and hair. It is a combination of lipids and other substances. It serves many essential functions, such as moisturizing the skin, protecting it, regulating the skin's pH, regulating body temperature, and promoting hair health. Understanding sebum is able to be beneficial for people who are planning or have undergone hair transplantation surgery.
• Theory of Donor Dominance: The theory of Donor Dominance is an idea in genetics that describes how particular genetic features or attributes of hair follicles used for transplantation are going to define the characteristics of the implanted hair. The theory of Donor Dominance suggests that the factors of the transplanted hair, such as texture, color, and rate of growth, are going to be determined by the characteristics of the donor's hair.
• Vasoconstrictor: Vasoconstrictor is a classification of medicament to narrow the blood vessels and to lessen the blood flow. It is used to reduce the bleeding throughout the hair transplant surgery. The hair follicles are extracted using a surgical procedure, and a Vasoconstrictor is utilized on the scalp. Additionally, it is used to treat many conditions, such as nasal congestion, hemorrhoids, low blood pressure, and shock. Individuals need to be mindful of Vasoconstrictors as they are able to have adverse reactions, which is not suitable for everyone.
• Vellus Hair: Vellus Hair pertains to the fine, short, and typically natural hair found on the donor site of the scalp. The hairs in the donor site are usually dense, healthy, terminal, thick, coarser, and more pigmented than vellus hair. The surgeon is able to gather vellus hair from the donor site and implant it at the recipient site. It is helpful when there is a lack of terminal hair in the donor site or if the recipient site has a high density of vellus hair. It is essential to be aware of vellus hair because it is possible to be used as a donor origin for implantation to a recipient site where hair is thinning or missing. It is necessary to comprehend the distinctions between vellus hair and terminal hair and the potential restrictions of utilizing vellus hair in hair transplant surgery.
• Vertex (Crown): Vertex (Crown) pertains to the back or top of the head. It is a usual site where hair loss or thinning occurs and is often a target site for hair transplantation. Vertex (Crown) is a complex site to treat because of the complicated anatomy of the scalp, and the positioning of the hair follicles in the area demands a high level of skill and accuracy. There are several keys to consider when planning a hair transplant procedure targeting the Vertex (Crown), including hair loss pattern, donor hair availability, and patient expectation. Knowing the unique difficulties and considerations connected with the vertex are able to help individuals make knowledgeable decisions about their hair loss treatment choices and able to help to ensure the best possible result of the hair transplant surgery targeting the Vertex (Crown).
• Vertex Transition Point (VTP): Vertex Transition Point (VTP) is a name used to explain the point on the scalp where the hairline at the front of the head meets the hair at the vertex of the head. It is an essential consideration in hair transplant surgery since it explains the whole look of the hairline and the allocation of hair thickness throughout the scalp. The Vertex Transition Point (VTP) is able to differ from person to person and is impacted by a diversity of factors, such as age, genetics, and hair loss pattern. It is necessary to consider the following factors when deciding the position of the Vertex Transition Point (VTP) in a hair transplant surgery, such as hair loss pattern, donor hair availability, patient expectations, and scalp anatomy.
It is essential to know the hair transplant-related concepts and definitions as they offer a structure for understanding many aspects of hair transplantation, such as the various procedures and methods used, the vocabulary usually used, and the possible dangers and advantages of the procedure. Possessing a clear understanding of the concepts and definitions able to help individuals create knowledgeable decisions about their hair loss treatment choices and are able to help to attain the best possible result of a hair transplant surgery. It helps the individuals to have a clear understanding of the procedure and are able to ask any questions or address any concerns they have.
How to Choose a Hair Transplant Clinic?
- Study the clinic's reputation: It is essential to find out about the feedback from past clients, ask for suggestions from the assigned dermatologist or other physicians, and check the clinic's certificate and credentials. Read their website or social media page feedback to learn more about the clinic. The number of followers means very little when verifying the clinic's quality. It is essential that the clinic has a license, is clean, and conditions seem safe.
- Consider the surgeon's experience and education: Consider a surgeon who passed the board and has comprehensive expertise in carrying out hair transplants. It is essential to ensure a first-rate team of licensed physicians and staff. It is one of the keys to a successful hair transplant procedure. Some of the clinic's website has information about the physicians or their medical credentials.
- Look at before-and-after pictures: It is essential to inquire about the before and after photos of the clinic's previous hair transplant client to acquire an idea of the outcome to expect. The clinic must be able to show clients samples and references of before and after pictures. It serves as proof of their work and success to their client.
- Consider the variety of hair transplant procedures: There are various hair transplant procedures, such as Follicular Unit Transplant (FUT), Follicular Unit Extraction (FUE), and Platelet-Rich Plasma (PRP). It is necessary to choose the clinic that provides the procedure that is ideally suitable to the particular needs and goals of the client.
- Discuss and consult: Arrange a discussion or consultation with the surgeon to discuss the objectives and problems and identify if the client is a good candidate for a hair transplant. Clinics with free consultations are highly suggested.
- Inquire about the follow-up care: Know what type of follow-up care is involved in the treatment plan and whether there are any extra rates for post-surgery care.
Get Your Hair Back with Best Hair Transplant Surgery

What are Board Certified Cosmetic Surgeons?
What are the Important Hair Transplant Certifications and Licenses for Clinics?
• Medical license: All hair transplant clinics must be managed by a licensed medical professional, including a dermatologist, plastic surgeon, or other specialists. It makes sure that a skilled and expert practitioner is overseeing the clinic. Attaining a medical license usually includes finishing medical school, finishing a residency program in a relevant specialty, and passing the United States Medical Licensing Examination (USMLE). Medical professionals with medical licenses are the ability to practice medicine in the state in which they are licensed.
• Clinical accreditation: Clinical accreditation is a process in which an external organization examines a hair transplant clinic to ensure that it meets specific quality and safety standards. A hair transplant clinic must be accredited by a known organization, including Joint Commission (JCI) or the International Society for Hair Restoration Surgery (ISHRS). A hair transplant clinic must undergo an onsite examination and meet specific criteria. It gives clients confidence in their care since it demonstrates that the clinic is dedicated to providing high-quality services.
• Insurance coverage: Hair transplant clinics need to have insurance coverage in the event of any accidents or complications during a procedure. It is able to protect the clinic and the patient. There are a few classifications of insurance that a hair transplant clinic is able to have, including professional liability insurance, medical malpractice insurance, and business insurance. Hair transplant clinics need to have the necessary insurance coverage to make sure that they have ready for any potential dangers or challenges that are possible to arise.
• Professional certification: The medical professional functioning at the hair transplant clinic must be authorized by an appropriate professional organization, including the American Board of Dermatology (ABD). It shows they have the essential education and expertise to conduct hair transplant treatments.
How to be a Hair Transplant Surgeon?
- Gain a bachelor's degree: It is an essential step to becoming a hair transplant surgeon. The aspiring surgeon must finish a bachelor's degree in an appropriate field, such as biology or chemistry, before applying to medical school. It gives an essential background knowledge and skills to succeed in medical school and beyond. A bachelor's degree involves completing research projects, internships, and other experiential learning and opportunities. It helps to prepare aspiring surgeons for the difficulties of medical school and a career in the medical field.
- Attend medical school: Apply to medical school after gaining a bachelor's degree. It takes four years to finish medical school. Med school is a postgraduate program that teaches students to become doctors or other medical professionals. It takes many classes and courses to understand the medical field, including pharmacology, anatomy, and physiology. It usually takes four years to finish. The standard exam needed is the Medical College Admission (MCAT) to the skill and knowledge of the student in the medical field.
- Pass the United States Medical Licensing Examination (USMLE): It is a three-step exam that examines an aspiring surgeon's knowledge of medical science, patient care, and professionalism. Individuals who want to take the USMLE must graduate from a medical school permitted by the Liaison Committee on Medical Education (LMCE) or the American Osteopathic Association (AOA)
- Completing a residency program: An eligible student who is able to apply for residency training in a surgical specialty, including plastic surgery or dermatology, is those who earned a medical degree. It usually takes four to six years to complete. A residency program is a postgraduate training program in which doctors and other medical professionals acquire hands-on experience in a specific medical specialty. Aspiring surgeon has the opportunity to earn hands-on experience during their residency in conducting surgeries and other medical methods. They are permitted to gain the essential knowledge and skills to practice individually and give top-rated care to their patients.
- Acquire a medical license: It is essential to get a medical license to practice as a hair transplant surgeon. The requirements to acquire a medical license are a complete a medical degree program, pass the USMLE, finish a residency program, and gain certification.
- Finishing a fellowship: A fellowship is a form of extra training and education that medical professionals are able to seek after completing a residency program. It is usually centered on a particular area of medicine and enables individuals to gain specialized skills and knowledge. An individual needs to have finished a residency program in a related field to complete a fellowship in hair transplant surgery. Fellowship programs for hair transplants are frequently intensely competitive and require applicants to have good grades, references, and medical practice.
- Acquiring certification: Acquiring a certification is an optional process that indicates that the aspiring surgeon has met the specific standards of learning and experience. An individual must meet some requirements to become board-certified as a hair transplant surgeon, including a valid medical license, educational and training requirements, and a certification exam.
There are various obstacles that hair transplant surgeons face in their practice. Surgeons face surgical risks since hair transplant surgery bears the risk of complications, including infection, bleeding, and scarring. The surgeons must be meticulous in lessening the chances and able to handle any possible problems. Additionally, surgeons face technical difficulties. A hair transplant procedure needs a high level of expertise and accuracy. They must be able to position hair follicles to attain a natural-looking outcome precisely. Moreover, surgeons need to meet their client’s expectations for the effects of their transplant procedure. They must be able to express realistically with clients about the restrictions and possible results of the surgery. Furthermore, surgeons face competition from other physicians since hair transplant surgery is a competitive field. Additionally, there are state and federal laws and regulations associated with medical practice, such as HIPAA and informed consent requirements, that surgeons must be conscious of and adhere to. Moreover, the hair transplant procedure is potentially not covered by insurance, as it is frequently considered optional and cosmetic. It is able to restrict access to surgery for some clients and affects the financial feasibility of the practice. Furthermore, surgeons must be updated on the latest research and development in hair transplantation. It includes continuous education and training to keep their expertise and knowledge.
Who is Hair Transplant for?

Why do People Need Hair Transplant Surgery?
What to Know about Hair Transplant Procedure?
Is It Safe to Get Hair Transplant Surgery?
Is Hair Transplant Surgery Painful?
What Is The Hair Growth Speed After Hair Transplant Surgery?
What is the Checking Frequency after Hair Transplant Surgery?
Can Supplements Treat Hair Loss?
How Do Hair Loss Reasons Affect Hair Transplant Process?
What Affects The Natural Look of Hair After Hair Transplantation?
How Is The Hair Transplant History?
What Is the Origin of Hair Transplant?
When is the First Hair Transplant performed?
What are the Examples of Before and After for Hair Transplant Surgery?

Follicular Unit Transplantation is a type of hair transplant procedure wherein the hair follicles are removed from the donor site, usually at the back of the head. Hair follicles are implanted in the recipient site, which is usually the scalp or face, where they are going to develop and produce new hair. The surgeons removed the hair follicles in a strip, dissecting them into single follicular units under a microscope.
The image below exhibits the before and after Follicular Unit Extraction (FUE).
Follicular Unit Extraction is a type of hair transplant procedure wherein the single hair follicles are removed from the donor site and implanted at the recipient site. The surgeons removed the hair follicles one at a time using a tiny and round punch with a diameter lower than 1 millimeter. The punch is implanted into the scalp to extract a hair follicle and then implanted at the recipient site.
Platelet-rich plasma (PRP) is a type of cure that includes injecting a concentrated solution of platelets into the skin or scalp. Platelets have development factors and other proteins that are able to encourage tissue repair and regeneration. PRP enhances the look of the skin to boost hair growth.
The image below exhibits Direct Hair Implantation (DHI) before and after.
Direct Hair Implantation is a type of hair transplant technique that involves the removal of the hair follicles from a donor site on the scalp and implantation at a recipient site where there is thinning or balding. The technique uses a unique tool to remove single hair follicles from the donor site and implant them directly into the recipient site.
A punch graft is a type of hair transplant treatment in which a tiny and round piece of the skin consisting of hair follicles is extracted from a donor site on the scalp and implanted in a recipient site where there is thinning and balding. It is called punch excision. The physician used a particular instrument known as a punch to extract round pieces of skin from the donor site. The size of the punch is the same as the single hair follicles. The tool is used to cut out a tiny and round skin section consisting of one or more hair follicles. The punch grafts are then implanted in the recipient site and positioned into small cuts created by the surgeon.
Neograft is a semi-automatic system for a hair transplant that utilizes a procedure known as Follicular Unit Extraction (FUE). It enables the harvesting of the follicles in FUE, which enhances the precision and speed of previously employed manual extraction devices. The NeoGraft system contains a portable apparatus to pull the hair follicles from the donor area and a particular device to insert the follicles into the recipient site.
Scalp Reduction is a medical method that includes extracting a section of the bald scalp and extending the rest of the skin to conceal the site. The technique is usually executed in people who experience male or female pattern baldness. It is usually joined with hair transplantation. The surgeon extracts a section of the bald scalp and stitches the rest of the skin to conceal the area.
Flap surgery is a classification of hair transplant method that includes moving a piece of scalp from the back or side of the head to the top or front of the head. The technique is usually executed in people with male or female pattern baldness. It is frequently joined with hair transplantation. The surgeon creates a cut in the donor site, extracts part of the scalp, and then implants it in the recipient area.
Scalp Expansion is a medical method that requires a balloon-like tool to expand the skin on the scalp. The procedure is usually conducted in people with male or female pattern baldness, and it is frequently combined with hair transplantation.
What are the Other Cosmetic Procedures similar to Hair Transplants?
• Scalp reduction surgery: Scalp reduction surgery is a procedure that includes the removal of a section of the scalp where there is thinning or balding and extracting the remaining scalp together to conceal the site. The treatment is used to lessen the size of a large bald area or hide the scars from past surgeries and injuries. The scalp reduction surgery is usually executed on a patient using local anesthesia to numb the scalp. The duration of the procedure depends on the size of the area being treated.
• Hair Integration: Hair Integration is a procedure that includes the attachment of artificial or human hair fibers to the scalp using a special paste. The fibers are able to be used to increase the volume and thickness of the hair, and they are able to conceal scars from past surgeries and injuries. It does not need any surgical incisions. The procedure duration depends on the amount of hair added, but it usually takes several hours.
• Scalp Micropigmentation: Scalp Micropigmentation is a procedure that includes tattooing pigment into the scalp to make the look of a complete head of hair. The process is frequently used to deal with hair loss or thinning hair, and it is able to be an effective method to enhance the look of thinning hair or a decreasing hairline. The professional used a particular machine to inject pigment into the scalp, and the pigment’s color depends on the individual’s natural hair. It is a non-surgical treatment and usually does not need any downtime. Qualified professionals in a salon or medical spa setting usually execute it.
• Laser Hair Restoration: Laser Hair Restoration is a classification of treatment that uses Low-Level Laser Therapy (LLLT) to encourage hair development and enhance the look of thinning hair. The treatment is usually used with a hand-held device that releases low-level laser light. The apparatus is passed over the scalp, and the laser light is taken by the cells in the scalp, encouraging blood flow and growing the creation of proteins essential for hair development. Laser Hair Restoration is a non-invasive treatment that replaces more invasive hair restoration treatments for people with light to moderate hair loss. It is not usually effective for people with progressive hair loss or baldness.
What is the Difference of Hair Transplant from Beard Transplant?
What is the Difference of Hair Transplant from Eyebrow Transplant?
What is the Forehead Reduction Surgery?
What are the Alternatives of Hair Transplant Surgery?
Get Your Hair Back @ HWT Clinic

Frequently Asked Questions
HWT Clinic's Blog
Welcome to HWT Clinic's Blog!