
Hormones are substances that are produced inside the body that partake in different kinds of processes and cause significant changes in the body. Hormones are involved in the daily regulation of the human body to maintain its structure and be able to respond accordingly to changing environments. One of the functions of these substances is seen in the hair follicles. They are responsible for the growth, development, and maintenance of hair follicles when they are kept at a normal range. However, hormones have the capacity to influence and damage the hair follicles when imbalances and abnormalities in terms of numbers happen. A sudden increase or decrease in hormones results in drastic hair problems. An example of a hair condition that is commonly associated with hormonal effects is hair loss.
Table Of Content
A hormone is a chemical messenger of the body that is formed by the endocrine glands of the endocrine system. A hormone circulates within the blood circulation and lands or binds on its individual marked cells or organs in the body. It is an essential regulator of diverse physiological functions in the inner and outer regions of the body, which include growth and reproduction, among others. It is divided into two kinds of hormones namely, steroid hormone and peptide hormone. A steroid hormone is defined as a lipid-soluble and hydrophobic chemical substance that is capable of penetrating deeply into the cell membranes. A steroid hormone binds to its designated receptors inside the cell and directly influences gene expression. Some common models of steroid hormones are testosterone and estrogen. Whereas a peptide hormone is a water-soluble and hydrophilic bodily entity that is made of amino acids. A peptide hormone attaches to the cell surface receptors only and does not have the capacity to go further inside the cell. It functions as an activator of a cascade of signaling units to stimulate a reaction. An example of peptide hormones is insulin and a growth hormone.
A hair follicle is a tiny arrangement in the skin that resembles a pouch and is the origin of fresh hair growth. A hair follicle in the scalp acts for the growth, maintenance, and eventual shedding of the hair. It is composed of the hair root, the blood vessels, and the sebaceous gland. The hair root refers to the region of the hair that is found inside the hair follicles, which is considered to be the living part and is responsible for the growth and nourishment of the hair strand. On the other hand, the blood vessels are the ones functioning as the supplier of demanded nutrients to both the hair root and cells around the area. Whereas the sebaceous gland is a small gland that functions as a lubricator of the hair and skin. 
The parts of hair follicles are listed below.
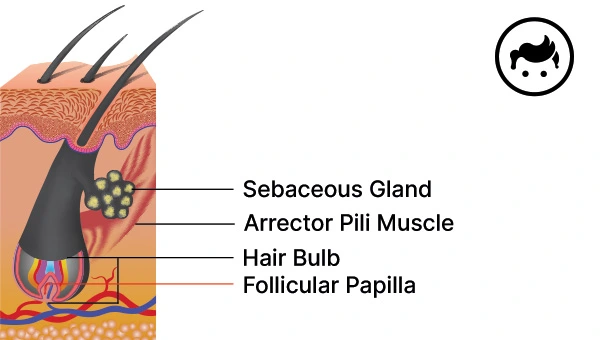
The sebaceous gland is a microscopic gland that lies in the hair follicles and releases a substance referred to as sebum. Sebum is an oil comprised of lipids such as wax esters, triglycerides, and scalene. It has the function of moisturizing the hair and skin to avoid dryness and dehydration. The sebaceous gland is prone to clogging; hence, it is great to keep it healthy by abiding by a skin and health care pattern. Apart from the scalp area sebaceous gland is evident in the face area, especially in the nose where it sometimes appears as a black dot due to the protruding sebum and is often misinterpreted as a blackhead.
The arrector pili muscle is a tiny, smooth muscle that resides at the base of each hair follicle. The arrector pili muscle has the role called piloerection, which is the ability of the hair to stand up. It contracts to stimulate the piloerection process. The events that influence piloerection are the following: cold environment, fear, and sexual attraction, among others. The arrector pili muscle is supported by the sympathetic nervous system, which is the part of the system that initiates the body’s “fight or flight” response. On top of that, the maintenance of body temperature is a task done by the arrector pili muscle by trapping a layer of insulating air next to the skin. Additionally, it is believed to be a part of sebum secretion along with the sebaceous gland.
The hair bulge is a small protrusion structure known as a bump that is located along the hair follicle. The hair bulge is consisting of numerous distinct kinds of cells, which include matrix cells and stem cells. The matrix cells are functioning for the synthesis of the hair strand. On the other hand, stem cells are responsible for keeping and regenerating the hair follicle. It is treated as the “active” part of the hair follicle, mainly because of its role in the growth and care of the hair strand. A deteriorated bulge is the reason for hair loss, thinning, and weakening. There are specific hair conditions that involve hair loss, such as alopecia areata that attack the hair bulb. Bulge is located in other body parts such as the beard, eyebrows, eyelashes, and pubic hair aside from the scalp.
The hair bulb is the base part of a hair strand and is found in the dermal layer of the skin. The hair bulb is constituted of cells that synthesize the hair shaft along with the melanocytes that induce pigmentation of the hair. Apart from that, the hair bulb has blood vessels that supply nourishment to the growing hair. The shape and size of the hair bulb are potential influencing factors to the shape and dense characteristics of the hair shaft. Pulling the hair bulb injures the hair follicle temporarily. However, a replacement bulb is created, and new hair is anticipated to grow in the same follicle.
The follicular papilla of the hair is a little, cone-shaped form that lies at the ground part of the follicle. The follicular papilla involves nerves, blood vessels, and connective tissues that nurture and deliver oxygen to the hair that is in the phase of development. The dermal papilla is another term used to describe the structure. It has a crucial position in the growth and development of hair, due to the cells that it holds that secrete hair shaft and pigment. The size of the follicular papilla has an impact on the consistency of the hair shaft. Larger papillae result in thicker hair.
People search which hormone promotes hair growth and hormones that promotes hair growth, contributing to thicker and healthier hair follicles in both men and women. The hormones that affect the hair follicles are listed below.
Testosterone is distinguished as a steroid hormone created mainly by the testicles in males, and the adrenal glands exude in the ovaries in females in a small number. Testosterone has a significant participation in the development of male reproductive tissues, namely the testis and the prostate. Apart from that, it has an influence on secondary characteristics of the male person such as increased muscle and bone mass, and the growth of body hair. Furthermore, testosterone is involved in hair development on the scalp which causes denser and coarser hair. On the other hand, a female person only secretes a small quantity of testosterone which is essential in the maintenance of libido and bone density. Men and women with a low level of testosterone result in decreased libido, osteoporosis, and muscle loss. However, excess of the male hormone leads to causing baldness, most notably the male pattern baldness that is extremely common in males.
Androstenedione is another steroid hormone where the origin of secretion is found in the testicles of males and ovaries of females. Androstenedione is sometimes referred to as androst-4-ene-3,17-dione. It is a predecessor hormone to testosterone and estrogen. Furthermore, it is spread out through the body by the conversion of 17-hydroxyprogesterone and is utilized in some dietary products. Androstenedione is treated to be a weak version of the hormone called androgen, which means that it consists of a weak ability to facilitate the development of male features. The hormone is thought to partake in the regulation of hair growth via its conversion to testosterone or estrogen. Although an increase in hair growth has been linked to elevated levels of androstenedione, the contribution of high levels of the hormone to hair loss is unclear. Some certain circumstances where there is an elevated level of the hormone cause the increase of potential risk of specific kinds of cancer. Androstenedione is restricted to be used by athletes imposed by the World Anti-Doping Agency (WADA).
Dihydrotestosterone is considered a metabolite of testosterone. Dihydrotestosterone is characterized as a hormone that is more powerful androgen than testosterone. It is created by 5-alpha reductase, which is an enzyme that transforms testosterone into DHT. It is recognized to partake in the development of male secondary sexual characteristics such as facial and body hair growth, and prostate enlargement that men often gain as they age. Dihydrotestosterone is an additional factor in the progression of male-pattern baldness. Excess hair growth commonly known as hirsutism and acne is linked to high levels of androgen dihydrotestosterone in women. Additionally, the hormone stimulates growth in places like the face and chest, but it results in hair loss on the scalp.
Dehydroepiandrosterone Sulfate or DHEAS is a steroid hormone where source of its secretion is found in the adrenal glands. Dehydroepiandrosterone Sulfate (DHEAS) is known to be the precursor of both testosterone and estrogen, which helps in regulating a wide range of physiological processes including hair growth. Low amounts of the hormone have been observed in a variety of hair disorders. Moreover, hair loss is linked to decreased levels of dehydroepiandrosterone sulfate which is related to aging. Notably, the hormone levels are utilized as a determiner that indicates an underlying condition like adrenal insufficiency or Cushing’s syndrome which has an influence on hair growth.
Hormones affect hair follicles in a series and distinct processes including hair growth, hair loss, and thinning hair. Hair growth is stimulated by several hormones such as testosterone and dihydrotestosterone (DHT), but excessive amounts of these hormones cause pattern baldness, hirsutism, and hair loss on the scalp. These two hormones promote hair growth and are responsible for the evolution of male secondary sexual characteristics. Apart from that, estrogens are great hair growth and thickness-promoting hormones. However, hair follicles are subject to lose or thinning by the decrease in estrogen levels. Insulin-like growth factor 1 (IGF-1) is another hormone that boosts the growth of hair. Proper regulation of hormones has significant benefits in achieving healthy and thick hair. Abnormalities in hormones are the main cause of hair problems both in males and females.
Examples of hormonal changes that affect hair follicles are listed below.
The benefits of hormones on hair follicles are listed below.
Yes, hormonal imbalances affect the function of hair follicles. Abnormalities in terms of hormonal levels often lead to hair issues such as hair loss, baldness, and hair thinning. An increase or decrease in the hormones is considered a hormonal imbalance and has a significant impact and changes the normal function of the body. For instance, a decrease in the amount of dehydroepiandrosterone sulfate (DHEAS) is known to lead to hair loss. It is the reason elderly people frequently encounter thinning or hair loss due to the significant drop in the level of dehydroepiandrosterone sulfate (DHEAS). Therefore, it is important to maintain and monitor hormones regularly by visiting and having a consultation with a licensed physician.
Yes, there are other factors that affect hair follicles aside from hormones. Firstly, genetics is known to impact individuals and predispose them to hair loss or other particular hair conditions. Male pattern baldness and alopecia are two common problems that are often caused by genetics. Secondly, nutritional deficiencies are causing hair problems due to a shortage of specific nutrients like iron, zinc, and vitamin D, which are important in normal hair growth. Thirdly, medications such as blood thinners, antidepressants, and birth control pills are known to result in hair loss side effects. Fourthly, chronic stress impacts hair growth and direct to hair loss. Stress is proven to be the reason for a temporary cessation of hair growth or disruption in the growth cycle. Lastly, age and medical conditions have both direct and indirect influences on hair follicles. Hair growth in elderly people is becoming slow, which means the hair is becoming thinner and potential breakage is expected. Meanwhile, medical conditions like autoimmune diseases and thyroid disorders are causing hair loss.
The phases of hair growth are listed below.
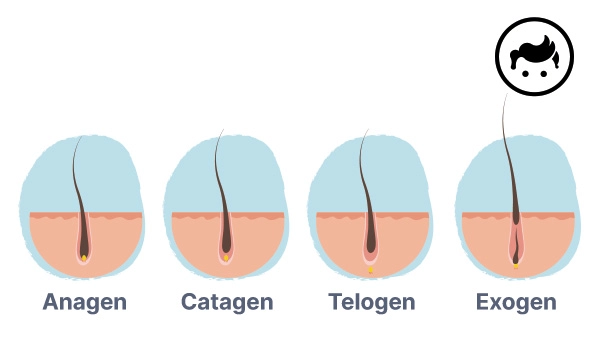
Anagen or the growing stage of the hair activity is where the hair vigorously develops. Anagen is recognized to be the stage that is the longest to end, which stays for about 2 to 7 years. The hair follicle’s cells increase in number quickly, forcing the hair shaft to break the skin’s surface and emerge from the follicle, during the step. Factors like genetics, age, and health all play a role in how long the anagen phase lasts. The hair is firmly attached to the hair follicle and does not come out easily within the anagen phase. Thus, hair growth during the step of anaphase is normally regarded as optimal.
The catagen phase ensues after the anagen and prior to the telogen. The catagen phase of the hair development revolution naturally stays between 14 and 21 days. It is a short stage where the hair is still affixed to the follicle, but it has discontinued developing and soon starts shedding. Catagen is a crucial stage of the hair cycle since it controls the whole procedure and gets the hair follicle ready for the next step of growth. The hair follicle reduces in size and the hair strand separates from its blood supply within the period. The result of the cell division cessation in the basal layer of the hair follicle is a keratinized hair strand.
Telogen or the resting phase is the stage that the hair strand is no longer vigorously increasing in length and is just anchored in the hair follicle slackly. Telogen is where a particular strand of hair has entered the stage where it is about to shed. The phase is expected to last between 60 and 120 days. Roughly 10 and 15 percent of the hair on the scalp is in the telogen phase at any particular time given. The hair follicle is inactive and disconnected from the hair root during the stage, which means it does not receive any blood supply. There is a degree of variability in the duration of the telogen step due to factors such as heredity, general health, and the cycles of hair development.
Exogen or the shedding phase is considered to be a continued stage of the telogen step of the hair cycle. Exogen stage is where the hair is experiencing shed from the scalp, which is aided by both washing and brushing. It is anticipated to occur from 2 months up to 5 months. The exogen stage is the final step of the hair growth process. Having to lose approximately 50 to a hundred hairs on a daily basis is a normal thing to have during the stage. However, new and fresh hairs are rising in the follicles to substitute for the fallen ones.
Yes, a lack of vitamins causes hair loss. A lack of particular vitamins results in hair problems such as hair loss because they play a vital position in preserving healthy, strong, and dense hair. Vitamins such as vitamin D is a very important nutrient since it helps in promoting hair growth by aiding the body to absorb calcium. Vitamin C maintains the hair strong by helping to produce collagen. Furthermore, vitamin A makes the sebaceous glands functional to produce sebum which is influential in moisturizing the hair. Additionally, vitamin E aims to aid in enhancing the circulation of blood to the scalp which is crucial in making the growth of hair faster. Shortage in these vitamins means that the normal function of the body is thoroughly regulated which results in hair loss.
Yes, estrogen causes growth in hair. Estrogen is a female sex hormone that partakes in the maturation and regulation of the female reproductive system. However, it is found to be beneficial in hair growth as it helps in prolonging the stage of growth in hair (anagen) and aids in elevating the diameter of the hair strands. The result is thicker and longer hair. Apart from that, it facilitates the rise of fine and vellus hair, which means a thicker head of hair and fewer hair loss problems are expected. It is important to note that imbalances and abnormalities in estrogen do more damage than good at preserving healthy hair.
Yes, progesterone cause growth in hair. Progesterone is another female hormone that maintains pregnancy and menstruation. It has an indirect function when it comes to the regulation of hair growth. Progesterone aids to balance the impacts of estrogen in extending the growth phase of the whole cycle. If you want to learn that does progesterone cause hair growth and it can influence hair health indirectly through its interaction with other hormones like estrogen, the answer is yes. It keeps the physiological processes of hair well-maintained and organized to avoid imbalances that result in hair issues. Hair loss, baldness, and hair thinning are expected without the presence of progesterone since estrogen is most likely to be destroying the anagen due to abnormalities.
The primary hormones that affect hair loss in females are androgens. Androgens are a pack of sex hormones that take effect in terms of reproductive health and body development. Some examples of androgens that have a significant impact and influence on hair loss in females are estrogen and dihydrotestosterone (DHT). Although estrogen and dihydrotestosterone (DHT) are known to be helpers and facilitators of hair growth, they are damaging when abnormalities and imbalances happen. Low levels of estrogen and unmaintained dihydrotestosterone (DHT) result in hair loss and other hair problems.
The hormone that affects hair loss in males is dihydrotestosterone or DHT. Dihydrotestosterone (DHT) is a product hormone of testosterone once it is transformed by an enzyme named 5-alpha reductase. The hormone does not directly serve as a hair-loss substance, but when it reaches an abnormal level, it has negative results which involve hair loss. The process by which dihydrotestosterone (DHT) damages the hair is through binding to the receptors of the hair follicles. It makes them shrivel, which leads to the stopping of hair production. The illness is named androgenic alopecia.
Hair loss problems caused by hormones can be seen in both women and men. When this type of hair loss problems reach an advanced level, Turkey hair transplant surgery may become necessary. In this case, a good hair transplant clinic should be chosen for cost-effective and quality service. In hair transplantation operations, Turkey has affordable hair transplantation costs. Turkey hair transplant costs and qualified clinics in Turkey should be researched for hair transplantation surgery.




